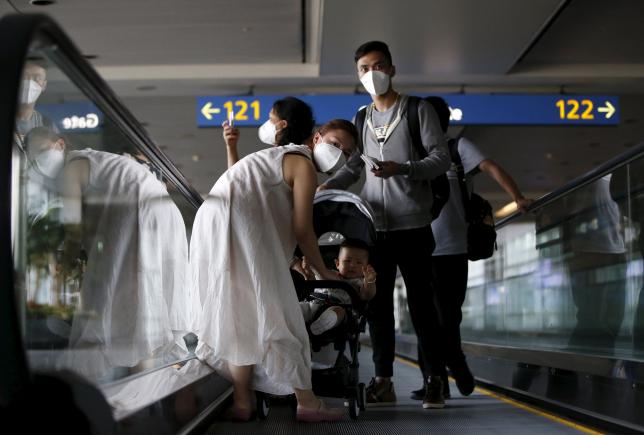
The recent outreak of the MERS virus in South Korea has raised major concerns since it has spread much faster than ever before, leading researchers to believe it might be a new super-spreader event.
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) is a viral respiratory disease caused by a unique coronavirus that was first identified in Saudi Arabia in 2012. You can tell from the name of the virus that it’s mainly located in the middle east and very rarley seen outside the area. Last month the disease managed to make its way to South Korea after a bussinesman picked it up in the middle east. This was the first time the disease was in the country. Apparently before health officials knew that he had MERS, he had already made his way to at least three hospitals seeking care and most likely spread MERS to more than 20 people.
In the past week South Korea’s confirmed cases of MERS have tripled to maybe more than 41, with at least three deaths. About 1,600 people are quarantined and more than 1,000 schools are closed. This has been the largest outbreak of MERS outside Saudi Arabia. Its managed to baffle researchers around the world who have been trying to figure out why the outbreak has spread so large, so quickly.
MERS has never been very contagious in the past at all. Surprisingly the virus is actually pretty lousy at spreading from person to person. On average, whoever who catches the virus passes it on to only one person, or even nobody.
This has lead to the big question, why is MERS suddenly spreading like a cold, or worse?
“What we now see in South Korea is kind of interesting and kind of worrying,” says Vincent Munster, who leads the viral ecology unit at the National Institute of Allergies and Infectious Diseases in Montana. “So we really have to figure out what’s going on there.”
A disturbing and kind of scary idea is that the virus has changed or mutated making it more contagious.
“It’s always possible that a virus can change. That’s a general rule,” says Christian Drosten, a virologist at the University of Bonn in Germany. “But such viruses usually need not just one but several of these changes [to become more contagious]. And the probability for these to happen together is really very, very low.”
The data collected so far in Saudi Arabia suggests that there are some patients that have exceptional high viral loads, which they can spread to sometimes a dozen or more. The thing about this super-spreader theory is that it’s very rare and if that’s the case the outbreak could be over in a week or so.
Outbreaks such as this are always a subject of concern. With the improvment of medicine in the past decades we’ve managed to put up a good fight against diseases. But this has led to the overuse of antibiotics and such, creating stronger bacteria and viruses that can resist more and more. If the doctors around the world would stop acting like your friendly neighboorhood drug dealer and wouldn’t prescribe antibiotics and strong medications for just a small cold and after only examining the patient for less than five minutes, then we might not be in this mess. Whatever the cause of this event has been, it directly relates to the democratic values of Life and Liberty. This is because it puts lives in danger and restricts peoples freedom to go wherever they wish to and do whatever they please.



VMU • Jun 5, 2015 at 1:58 pm
this sounds horrible is the Government doing something about this?