From the Pearl Harbor Bombing to the Nuclear Age in Asia
How did World War II create a nuclear age in our world?
The war for the United States began with the Japanese bombing of Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941 but it ended with the United States being the first and only nation to drop 2 atomic nuclear bombs on major cites. The American fight against the Japanese during the early 1940s brought the dawn of the “nuclear age”.
President Roosevelt had the US Pacific Fleet move to Pearl Harbor in 1939 and Japan wanted to expand in the Pacific. Military leaders and politicians saw a war going on between Japan and the United States and decided to attack first. Japan bombed Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941.
2,403 people were killed and 1,178 people were injured from the bombing.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uzdoo__v5Ew
The United States tried to avoid World War II as it was going on, but the attack on Pearl Harbor forced the US to join World War II. Although World War I was the first war that involved aircraft, it was during World War II where aircraft took a major role. There were three major types of planes, fighter planes, bombers, and transport. Fighter planes were made for air to air combat. Bombers where designed to carry and drop bombs on enemy targets. The transport planes were made to carry troops and supplies to take around the world. Transport planes where important during the war, many of them where civilians planes used by the air force for the war.
Throughout the war new technology emerged but none proved more powerful than the atomic bomb.
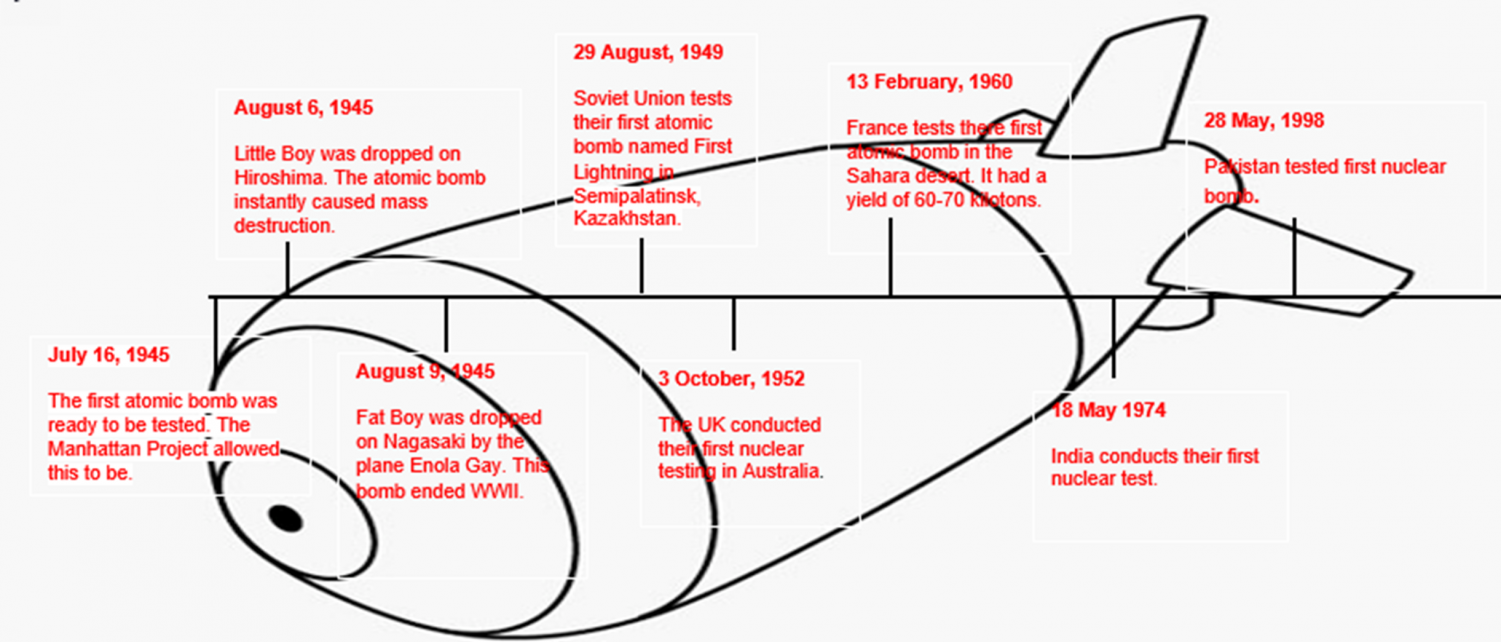
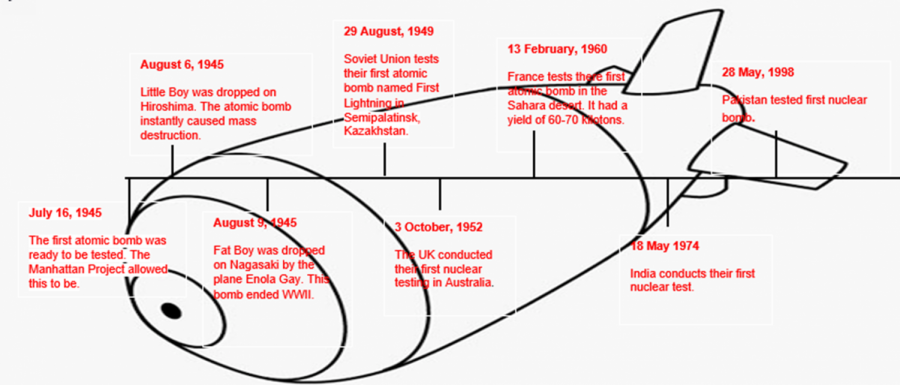
 What was the “Manhattan Project? How did the atomic bomb come to be? The Manhattan Project was research and development project during World War II for a nuclear bomb. The project began in 1939 and ended in December 31, 1946. By July 1945 a prototype was ready for testing and on the July 6, 1945 the first atomic bomb was dropped for testing in a desert.
What was the “Manhattan Project? How did the atomic bomb come to be? The Manhattan Project was research and development project during World War II for a nuclear bomb. The project began in 1939 and ended in December 31, 1946. By July 1945 a prototype was ready for testing and on the July 6, 1945 the first atomic bomb was dropped for testing in a desert.
President Truman’s decision led to thousands of deaths. Although it was a harsh decision it wasn’t an easy one. There were many different factors when Truman was making this decision.
Truman was “eager” to drop the bomb, he writes, and was unwilling to explore alternatives for three reasons.
First, Truman wanted to avoid a land invasion of Japan, which would have killed thousands of Americans.
Second, he was determined to impose unconditional surrender on the Japanese because anything short of that would have made him appear weak. He also worried that a failure to achieve unconditional surrender might fortify those in Japan who wanted to continue fighting.
Finally, Truman hoped to end the Pacific War before the Soviet Union entered the fray against the Japanese, a development that might permit Stalin to obtain territory in Asia or demand a role in America’s postwar occupation of Japan. Consequently, Truman was in a hurry to use the bomb.
-Tsuyoshi Hasegawa’s “Racing the Enemy: Stalin, Truman, and the Surrender of Japan,” a landmark book that brilliantly examines a crucial moment in 20th-century history.
https://www.csmonitor.com/2005/0802/p17s01-bogn.html
2 separate atomic bombs were dropped on two Japanese cities named Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The bomb dropped on Hiroshima, on August 6, 1945, caused severe destruction and immediately killed 150,000 people. The bomb exploded with an energy of 15 kilotons. The second bomb dropped, Nagasaki, killed 75,000 people. The two bombs ended the war.
What happened in Japan during the years following World War II? Do they have nuclear technology today? When did they get access to it? After world war 2 the allied powers of Great Britain, the Soviet Union, the Republic of China, and the United States discussed how to disarm Japan, deal with its colonies, stabilize the Japanese economy, and prevent the re-militarization of the state in the future. Japan currently does not have any nuclear bombs. They are banned from having a military and nuclear technology. The demilitarization of Japan and the protection of the United States’ nuclear umbrella led to a strong policy of non-weaponization of nuclear technology. here
How did countries such as Pakistan and India who were once under the control of the British empire during World War II become nuclear powers today?
As World War II was coming to an end many countries started becoming independent and forming governments. It was expected that after the war the British colonies would soon disintegrate. The Pakistan Movement was led by Muhammad Ali Jinnah and resulted in Pakistan becoming a Muslim state. Pakistan gained its independence on August 14, 1947. India’s independence came right after that on August 15, 1947. on June 15, 1947 the British House of Commons passed the Indian Independence act, or Mountbatten Act. This act divided India into two dominions. India and Pakistan was granted independence. Muslims ignored attempts to include them in an Indian government lead by Hindus. Riots broke out between the Muslims and Hindus in multiple Indian cities. In August 1946, four days of fighting left more than 5,000 dead and more than 15,000 hurt in Calcutta. Partition is when a country is divided in two and then would form two separate governments and the British were finally convinced that the only way to solve this bloodshed would be to do that.
When did Asia enter into the nuclear age?
- Russia. After Soviet leaders learned that United States and Germany had embarked on efforts to build an atomic bomb they decided to also start creating the atomic bomb. In February 1943, the Soviets began their own program led by nuclear physicist Igor Kurchatov and political director Lavrentiy Beria. The Soviet atomic program was tiny compared to the Manhattan project with approximately 20 physicists and a small number of staff. On August 29, 1949 the Soviets successfully tested their first nuclear device, called RDS-1 or First lightning.
- China started developing nuclear weapons in the late 1950s with help from the Soviets. In the 1960s China made remarkable progress and a 32 month period China successfully dropped its first atomic bomb on October 1964.
- India’s nuclear weapons program started at the Bhabha Atomic Research Center. India’s first nuclear test named Smiling Buddha was dropped on May 18, 1974.
- Pakistan. In the mid 1970s Pakistan gained access to uranium and were on the path to atomic weapons. Shortly after India had tested their atomic bomb Pakistan conducted their first test in May, 1998.
- Iran In 2015 a deal was made called Iran’s nuclear deal. The agreement was that Iran would stop trying to make nukes and the US and allies would go lightly on the sanctions. But now the deal is over and President trump says the US is going to put harsh sanctions on Iran and its big export oil. That means higher gas prices in the US.
- Israel- in 2016 an email was leaked saying there were “200” nuclear weapons in Israel. Although that number is most likely a exaggeration Israel has nuclear weapons. They joined the nuclear club in the 1950s.
- Korea conducted their first atomic bomb test on October 9, 2006. On October 3, 2006 it was announced that a nuclear test would be happening.
The nuclear age has its pros and cons. Being able to use the nukes as a threat can help stabilize other nations. But are the pros really greater than the cons? If a nuke was to be used millions of people would die and for what? What about the effects it would cause to the environment? Having nuclear weapons is a great and reliable source for power and status but it also has serious effects that come with it. Why do innocent civilians need to die if war has broke out? Why should people live in fear that a bomb could hit them and kill them at any time? In my opinion the nuclear age was a good thing to help with other nations and keep them in check and also make a stand if other nations make threats. But in the end is it worth all the damage that it could do?