John Locke’s Ideas on Property in a Modern World

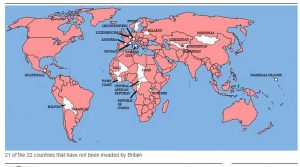
John Locke was an Enlightenment thinker from England who has had a very big influence on the modern ideas of democracy and property. This “father of liberalism” as he is commonly known could not have imagined our current world of 7.6 billion people. He lived just over 300 years ago but his world was far different. In the world of 1700 there were less than 1 billion people and the nations were controlled by empires. He spoke about property from the point of view of the English who had the power to control property anywhere they went in the world. The British had claimed or were claiming property for their own on every continent.
 What is the state of nature? This is an idea that British philosopher John Locke and other thinkers like him used to talk about human rights. He imagined that all humans are born with equal rights but these rights were not protected. Everyone has life, liberty and the right to property but these rights must be protected by governments. It is up to the people to create good governments and when the governments are bad the people can fight for their rights by creating a better government.
What is the state of nature? This is an idea that British philosopher John Locke and other thinkers like him used to talk about human rights. He imagined that all humans are born with equal rights but these rights were not protected. Everyone has life, liberty and the right to property but these rights must be protected by governments. It is up to the people to create good governments and when the governments are bad the people can fight for their rights by creating a better government.
John Locke said all men were created with a natural right to property. In America we interpreted this as “the pursuit of happiness” when Thomas Jefferson referred to Locke’s ideas in the Declaration of Independence in 1776. Often people only think about rights as freedoms or liberties. What if we thought of a “statue of responsibility” every time we thought about the “statue of liberty”?

The image to the left shows a model of a “Statue of Responsibility”. Why does it show two hands holding onto each other? Why is one hand reaching up and the other down? This could be to show how people are not equal and it is up to those who have more to reach down and help those who have less. this is like the poem inscribed on the statue of liberty that welcomes the poor and the immigrant to the USA.
John Locke was an Enlightenment thinker who said all human beings have natural rights like Life, Liberty and Property. With all rights come responsibilities. The enforcement of rights and responsibilities is called justice and is usually done with the use of an agreement or “social contract”. When governments like the United States try to protect the natural rights of their citizens they do it with civil rights as listed in the US Bill of Rights but what about the idea of a global social contract? Do all human beings have a natural responsibility to one another?
What does John Locke say about property and natural rights?
Locke’s natural right are LIFE, LIBERTY AND PROPERTY. Locke believed that the most basic human law of nature is the preservation of mankind. He believed that both individual have the a right and duties to preserve their own life and property.
What are natural rights? is the right for human beings to be treated equally regardless of race, religion, ethnic, gender, background, or sex orientation. we are all equal and we all the same right either rich or poor. Do we really have these right today? NO. Most women, children and poor people have been treated today unfairly in our society there right has been take from them by those with the money and power.
So how do we move forward? This is the continued struggle for civil rights and it brings up issues of justice known as distributive justice. What is distributive justice? It has to do with ownership and how goods are acquired.
Equality = opportunities and outcomes
Proportionality = equal work and equal outcomes
Fairness = one group is not more privileged than another or controlling most goods at the cost of another.
https://www.wider.unu.edu/publication/global-distribution-household-wealth
What is consumerism?
Consumerism is an economic theory which states that a progressively greater level of consumption is beneficial to the consumers. Since the 1800s and the Industrial Revolution the world has been consuming at a higher rate than ever.
Wealth and standard of living= refers to the level of wealth, comfort,material, goods and necessities available to a certain social economic class in a certain geographic.
What does it mean when people choose wealth over virtue?
Today we need to learn how we can reform our consumerism to consume goods and services that help one another rather than just make one group happy while making life difficult for another group.
The environmental effects of consumerism =
Effects of consumerism on the environment: Pollution and resource depletion
As well as obvious social and economic problems, consumerism is destroying our environment. As the demand for goods increases, the need to produce these goods also increases. This leads to more pollutant emissions, increased land-use and deforestation, and accelerated climate change. We are experiencing devastating effects on the planets water supplies, as more and more water stores are used up or diverted as a part of intensive farming procedures.Waste disposal is becoming a problem worldwide, and our oceans are slowly but surely becoming a giant waste disposal pit. It is estimated that over half of the plastic produced every year is single use – this means that it is used once, and then either thrown into landfill or finds its way into the environment. According to scientists, up to 12 million tons of plastic enters the ocean every year, forming giant floating garbage patches all over the world.
What can we do?
It is obvious that we need to reduce consumerism and change our current lifestyles, otherwise the planet we know will cease to exist. We are currently consuming resources at an unsustainable rate, which is causing mass environmental destruction and social problems across the world.
Make a change today by reducing materialistic possessions, increasing recycling, and raising awareness in your community.
What is the responsibility we have that balances out the “right to own” property?
example: recycling
How do we define environmental sustainability? Is the state in which the demand place on the environment can be met without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.
What would John Locke say about environmental sustainability


JOHN LOCKE QUOTE ABOUT NATURAL RIGHT 
How land is used to produce food etc. can have enormous impacts on the environment and its sustainability. (This can sometimes challenge assumptions on the instinct and common belief that we are overpopulated by sheer numbers and that this is the major cause of environmental degradation. While populations can burden the environment, the most populous regions in the world use far less resources than the wealthiest nations, and so the issue is more about how resources are used and for what purpose.)
Stephenson and colleagues posit that it is numbers of consumers rather than people per se who need to be factored into the scenarios. Demographers project that most of the population growth we’ll see by mid-century will occur in poorer countries that consume less than their wealthier counterparts. However, growth in consumption is exceeding growth in population in developing and developed countries alike.
The study concludes that promoting sustainable lifestyles and reducing consumption in wealthier countries will help lower carbon emissions, with health benefits extending to poorer countries
“Demographics, consumption, and climate change.” The Futurist, Mar.-Apr. 2014, p. 4. Academic OneFile, http://link.galegroup.com/apps/doc/A360611646/AONE?u=fairfaxcps&sid=AONE&xid=36ae4803. Accessed 23 May 2018
https://study.com/academy/lesson/distributive-justice-definition-theory-principles-examples.html










